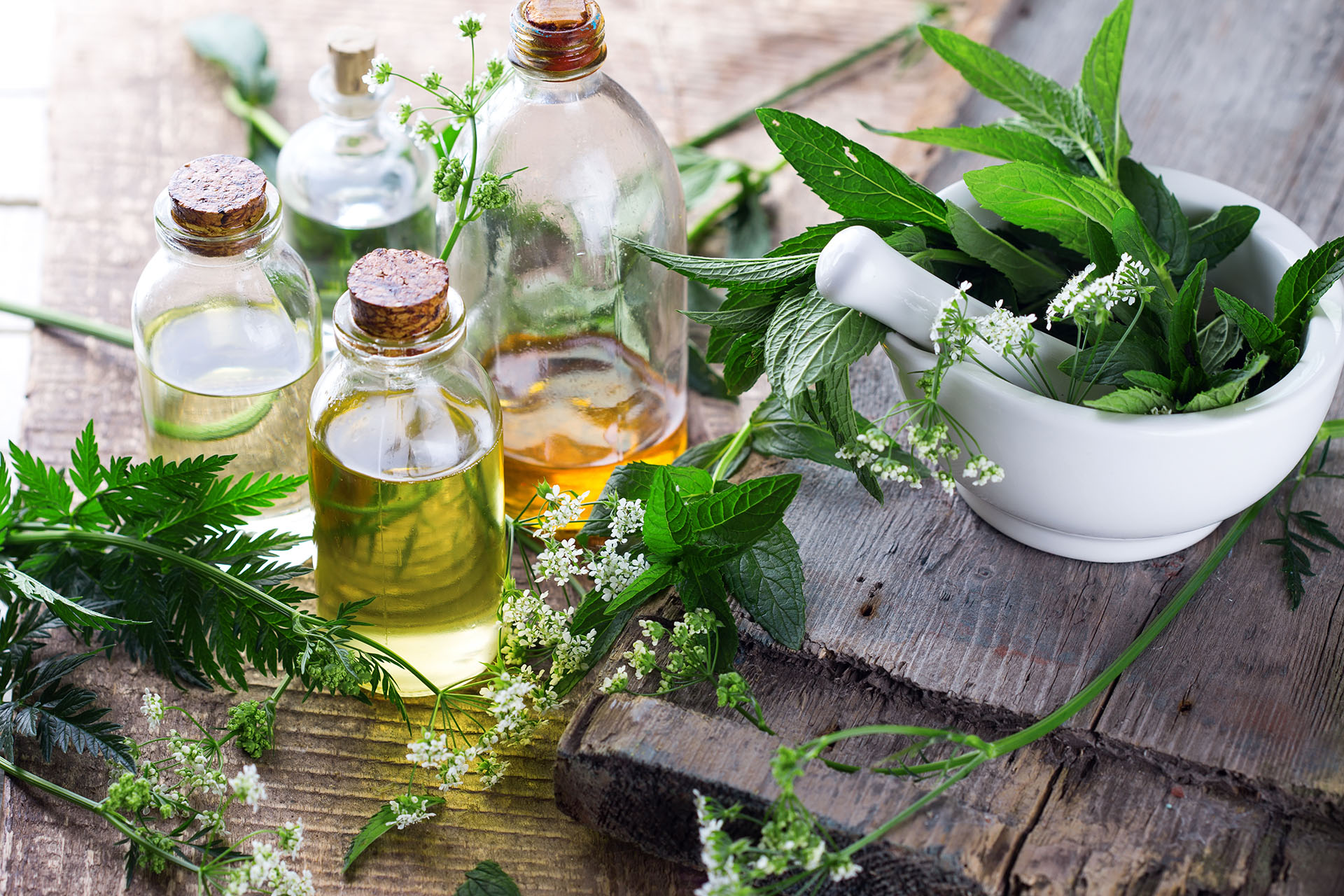
Herbal medicine, a cornerstone of traditional healing practices, has been utilized by cultures worldwide for thousands of years. Drawing on the natural properties of plants, herbal medicine offers a holistic approach to health and wellness, emphasizing the body’s ability to heal itself. As modern science increasingly validates the efficacy of many herbal remedies, there is a growing interest in integrating these ancient practices into contemporary healthcare. This exploration of herbal medicine delves into its history, principles, and practical applications, highlighting the enduring relevance of plant-based healing in our modern world.
The roots of herbal medicine can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as China, Egypt, India, and Greece, where plants were revered for their therapeutic properties. In these cultures, healers and herbalists meticulously documented the medicinal uses of various plants, creating extensive pharmacopeias that guided their practices. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Ayurveda, and Western herbalism are among the most well-known systems that have evolved over millennia, each with its own unique philosophies and methodologies. Despite their differences, these traditions share a common belief in the synergy between the human body and the natural world, advocating for treatments that restore balance and harmony.
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, the concept of qi (pronounced “chee”), or vital energy, is central to understanding health and disease. TCM practitioners believe that illness arises from imbalances or blockages in the flow of qi, and that herbs can help restore equilibrium. TCM employs a wide range of plants, roots, and fungi, often combining them into complex formulas tailored to individual needs. For instance, ginseng, known for its adaptogenic properties, is used to boost energy and resilience, while licorice root is often included to harmonize and enhance the effects of other herbs. This holistic approach considers not only the symptoms but also the underlying causes of illness, treating the body as an interconnected system.
Ayurveda, the ancient healing system of India, also places a strong emphasis on balance, particularly the equilibrium of the three doshas: Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. These doshas represent different combinations of elemental forces within the body, and their balance is essential for health. Ayurvedic practitioners use a variety of herbs to address imbalances and support the body’s natural healing processes. Turmeric, for example, is prized for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, while ashwagandha is valued for its ability to reduce stress and enhance vitality. Ayurvedic treatments often include dietary recommendations, lifestyle changes, and herbal formulations tailored to an individual’s unique constitution.
Western herbalism, rooted in the healing traditions of ancient Greece and Rome, has evolved over centuries to incorporate insights from European folk medicine and modern scientific research. Pioneers like Hippocrates and Galen laid the groundwork for this tradition, emphasizing the importance of diet, lifestyle, and natural remedies in maintaining health. Today, Western herbalists utilize a diverse array of plants to support wellness and treat illness. Echinacea, for instance, is commonly used to boost the immune system and prevent colds, while St. John’s Wort is renowned for its antidepressant properties. The integration of herbal medicine with conventional healthcare in many Western countries reflects a growing recognition of its value and potential.
The therapeutic potential of herbal medicine lies in the rich array of bioactive compounds found in plants. These compounds, including alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, and polyphenols, interact with the body in complex ways, offering a wide range of health benefits. For example, the anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, have been extensively studied and shown to be effective in managing conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Similarly, the antioxidant effects of resveratrol, found in grapes and red wine, contribute to cardiovascular health by protecting against oxidative stress and reducing inflammation.
One of the key advantages of herbal medicine is its holistic approach, which considers the whole person rather than focusing solely on symptoms. This perspective recognizes the interconnectedness of body, mind, and spirit, and aims to address the root causes of illness. For example, an herbalist might recommend adaptogenic herbs like Rhodiola or Holy Basil to help the body cope with stress, recognizing that chronic stress can contribute to a wide range of health issues. By supporting the body’s natural ability to adapt and heal, herbal medicine promotes resilience and long-term well-being.
Herbal medicine also emphasizes the importance of individualized treatment. Unlike standardized pharmaceuticals, which are often designed to target specific symptoms or conditions, herbal remedies can be tailored to an individual’s unique needs and constitution. This personalized approach takes into account factors such as age, gender, lifestyle, and overall health, allowing for more nuanced and effective treatments. For instance, a herbalist might create a custom blend of herbs to support a person’s immune system during flu season, considering their specific vulnerabilities and health history.
Safety and efficacy are paramount in the practice of herbal medicine. While many herbs are safe when used appropriately, it is essential to recognize that they can also interact with conventional medications and cause side effects if misused. Consulting with a qualified herbalist or healthcare professional is crucial to ensure that herbal treatments are safe and effective. Additionally, sourcing high-quality herbs from reputable suppliers is important to avoid contamination and ensure potency. As the popularity of herbal medicine grows, so does the availability of standardized extracts and supplements, which provide reliable dosing and convenience.
Modern scientific research continues to explore and validate the therapeutic potential of herbal medicine. Studies have shown that herbs like ginger can effectively reduce nausea and vomiting, while ginkgo biloba can improve cognitive function and memory in older adults. The antimicrobial properties of garlic have been demonstrated in numerous studies, highlighting its potential as a natural antibiotic. These findings support the traditional uses of these herbs and provide a scientific basis for their inclusion in modern healthcare.
Integrating herbal medicine with conventional treatments can offer a complementary approach to health and wellness. For example, herbs like milk thistle can support liver health and enhance the body’s detoxification processes, potentially benefiting patients undergoing chemotherapy or taking medications that strain the liver. Similarly, the use of valerian root for anxiety and insomnia can complement conventional treatments, providing a natural alternative for those seeking relief from these conditions. This integrative approach recognizes the value of both traditional and modern medicine, offering a more comprehensive strategy for managing health.
Despite the many benefits of herbal medicine, it is essential to approach it with an informed and cautious mindset. Self-diagnosis and treatment with herbs can be risky, particularly for individuals with chronic conditions or those taking multiple medications. Seeking guidance from a qualified practitioner ensures that herbal treatments are safe, appropriate, and tailored to individual needs. Education and awareness are key to harnessing the full potential of herbal medicine while minimizing risks.
Herbal medicine represents a rich tapestry of ancient wisdom and modern healing, offering a holistic approach to health that is both timeless and timely. By embracing the therapeutic properties of plants, we can support our body’s natural ability to heal, enhance overall well-being, and address the root causes of illness. Whether through the traditions of TCM, Ayurveda, or Western herbalism, the use of herbs provides a powerful tool for maintaining health and promoting resilience. As we continue to explore and integrate herbal medicine into contemporary healthcare, we honor the enduring legacy of plant-based healing and its profound potential to support and sustain life.